Enterprise risk management
E-BI has a wide range of stakeholders. In order to present representative stakeholders, E-BI refers to the five aspects of the AA1000SES Stakeholder Engagement Standard (AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard 2015): dependence, influence, and attention. , responsibilities and multiple perspectives were identified, and finally nine categories of stakeholders were screened out according to their importance. They are: employees, customers, suppliers, (investor) shareholders, governments and competent authorities, non-profit organizations, research institutions, communities, media and other stakeholders, and are supplemented by correlation tests every year to review the responses to the stakeholder questionnaires. , the communication results are reported to the board of directors by the ESG department. In 2024, E-BI will continue to stimulate different results and generate diversified social values with nine types of stakeholders through regular and irregular communication channels. Issues of concern to each stakeholder group are also communicated through the corresponding chapters of this report.
Risk management topics
E-BI refers to the risk issues faced by domestic and foreign companies, and takes stock of the division of responsibilities within the internal organizational structure to develop a clear and complete risk classification framework to ensure that it can include various risk projects at different levels, and accordingly develops the economy (including companies Governance), environment, society and others, and divided down into eight major risks, the scope of which is described in the figure below.
Four aspects Eight major risks
Environment
- Environmental Risk
Society
- Occupational Hazard Risk
- HR Risks
Economic Governance
- Market Risk
- Operational Risk
- Investment Risks
- Regulatory Compliance Risks
Others
- Other Risks
Risk management system and risk identification
In 2024, E-BI will use the two risk issues of "power outage" and "infectious diseases" as priority projects for the introduction of ERM projects. Its implementation content includes establishing ERM baselines, setting ERM performance indicators, conducting education and training, and completing ERM procedure documents. and work instructions, etc., and through the establishment of procedures and work instructions, set risk tolerance, conduct risk assessment operations, establish an ERM document control mechanism, and propose risk improvement measures. Mainly divided into 6 steps:
-
1.Inventory the power structure of the factory: First, conduct an inventory of the power structure used in the production plant to understand the current power supply sources, including the main power source and the system operation of backup power, such as single and double circuits, generators and green Electricity usage, etc.2.Abnormal analysis of historical events: Collect information on the causes, frequency, and impact of past power outages in the factory area to establish a baseline for power outage risk events.3.Analysis of possible potential causes: Use systematic methods such as fishbone diagrams to find out the known, potential and unknown risks of power interruption in terms of people, machines, materials, methods, environment and other aspects.Impact assessment of abnormal occurrences: Establish a risk assessment matrix through the two dimensions of frequency and severity of power outages to identify the main risk sources that have a greater impact on the company.Propose improvement control plans: Propose feasible prevention and improvement plans for the main risk sources after impact assessment, including planning green power solutions to prevent risks caused by power shortages, or ensuring power supply contracts, production line transfers and factory sites through signing Implement energy conservation and carbon reduction projects to reduce the impact of power outages.Power interruption risk assessment: After implementing the planned improvement control plan, continue to conduct risk assessments to minimize the risk of power interruption using the PDCA cycle.

Epidemic trigger / information disclosure

E-BI’s Infectious Disease Risk Assessment Process, mainly refers to the EU ECDC Rapid Risk Assessment Operational Guidelines for Infectious Diseases (2019), and is divided into 5 steps. The instructions are as follows:
- Preparation period: Understand the definition of infectious diseases in advance, and organize domestic and foreign policies and regulations on infectious diseases, health units and company internal information
- Collect epidemic information: Collect epidemic situations that have occurred inside and outside the factory area, and take inventory of epidemic-related information handled by internal responsible units.
- Comparison of international trends: Browse the epidemic information released by the WHO online, and compare the epidemic information collected by the factory with the content released by the WHO.
- Confirm the epidemic: After comparing international trends, if it is found that sporadic cases may or have already occurred in the factory location, the infectious disease will be recorded and used as the basis for subsequent risk assessment.
- Risk assessment: Set the severity level according to the types of infectious diseases defined by the government, and identify which infectious diseases with high risk through risk matrix assessment to start subsequent preparations.
Confirmation of improvement measures, risk monitoring and internal audit management review. Regarding the proposed power interruption and infectious disease prevention/improvement measures, document review will be carried out through the implemented form records. Epidemic triggers/information disclosure includes the qualification certificates and regulations of the operators. /Compliance inspection results, operation management methods and procedures, relevant meeting notices and records, etc., and an internal audit review mechanism will be planned.
Long-term emerging risk management:
Environmental risks:
E-BI's main production base is located in mainland China. However, affected by climate change, infectious diseases, and geopolitical issues, China's power supply shortage has become one of the risks to the company's production and operations. In addition, some of E-BI's customers It is also hoped that companies can set carbon reduction goals and require the use of renewable energy to achieve low-carbon production. Therefore, how to deploy renewable energy in advance has become one of the emerging risks faced by E-BI.
Geopolitical risks:
The Sino-US trade war that broke out in 2018 has not yet stopped. Coupled with the impact of the new coronavirus and this year’s (2022) Russia-Ukraine military war, it has brought major impacts to the global economy. For companies whose manufacturing bases are mostly in mainland China and whose trade exports are mainly in the United States and Europe, the business environment they face is even worse. In addition to facing problems such as insufficient supply of raw materials, rising prices, and labor recruitment, They must face fluctuations in interest and exchange rates caused by trade barriers. Therefore, how to reduce operational and financial risks caused by geopolitics has also become an emerging risk issue in recent years.
Management of human rights
E-BI and all management understand that compliance with international labor standards and protection of labor rights are essential for a responsible company and are the expectations of stakeholders such as consumers, customers, the public and governments. The Company is committed to comply with national labor laws and regulations, internationally recognized labor standards, and other applicable international conventions, and to continuously improve working conditions and employee welfare, with a view to establishing, implementing and maintaining a good human rights management system, and extending this code to suppliers and contractors.
Human rights policy:
E-BI respect and support internationally recognized human rights norms and principles, including the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the United Nations Global Covenants and the International Labor Organization's Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work, adhere to the legal norms of the company's location, and develop E-BI human rights policies in accordance with the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights
Human rights commitments:
1.we firmly believe that respecting and protecting human
rights is an important foundation for the sustainable operation of
enterprises.
2. we take human rights issues into account in all aspects of our
operations.
3. we provide smooth communication channels for stakeholders.
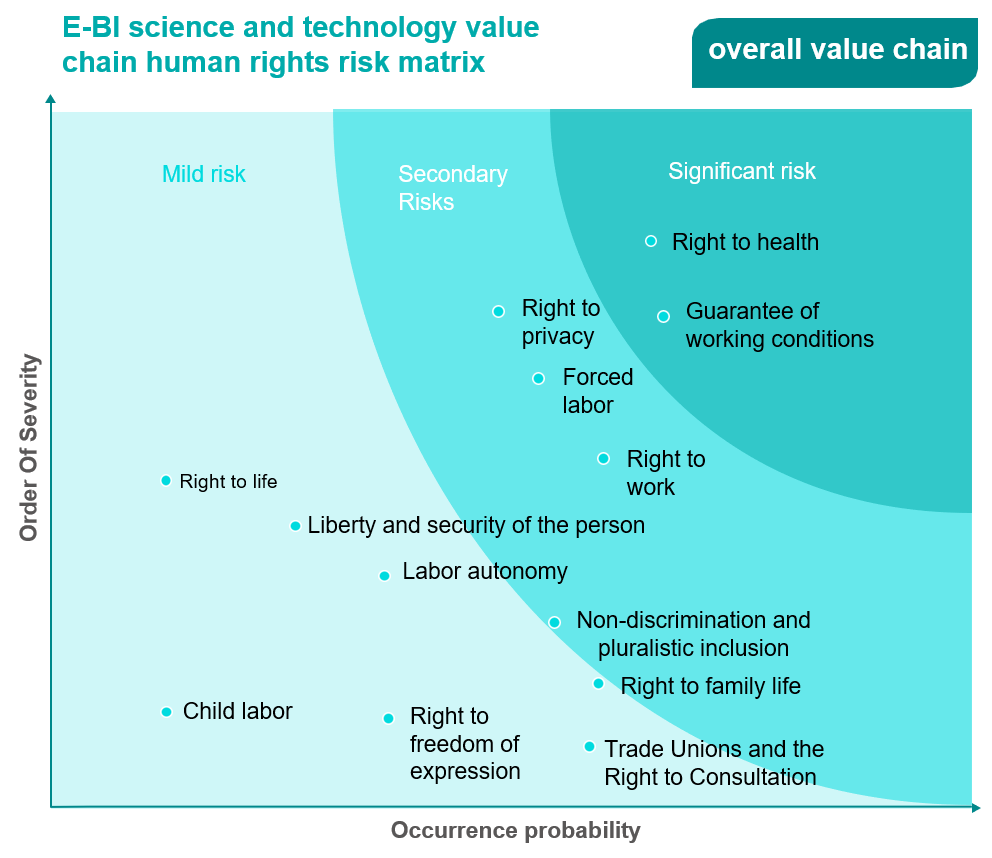
Human Rights Risk Identification Process
Identification of human rights risks
In order to identify the adequacy, effectiveness and suitability of the Company's social responsibility management system, and to check the compliance of system policies, objectives and regulations, internal and external audits of the plant are regularly implemented in accordance with RBA audit procedures. The audit process clearly defines responsibilities, behavioral procedures, audit implementation methods and cycles, audit reports and non-conformance improvement tracking. The code of conduct of the responsible business alliance includes the standards of labor, health and safety, environment and corporate ethics. According to this rule, the company has set up an RBA committee organization, held monthly self-inspection discussion meetings, continuously improved RBA management level through mutual experience exchange, and arranged internal audit to ensure compliance with the standard. In case of non-compliance with the project, improvement plans must be put forward within the deadline for improvement. In addition, the Company's procedures, regular internal and external audits, and annual management review meetings, review the achievement and improvement of labor, ethics, environment, safety and health performance indicators to ensure that the Company fulfills its social responsibilities. Periodic human rights questionnaires are also conducted with external value chain partners (customers, suppliers, contractors, local communities, etc.).